Insurance role in addressing climate change and sustainable development
Extreme weather is becoming more often due to climate change, and we are at risk. Major threats include drought, flooding, extremely high temperatures, and cyclones, which might be disastrous. As weather events become more severe, the cost of environmental disasters will make sustainable development nearly impossible worldwide unless more is done to reverse this situation and build resilience.

This significant challenge in sustainable development calls for immediate action. The insurance sector needs to play a pivotal role in helping to promote both adaptation and mitigation.
Mitigation
As underwriters and long-term capital managers, insurers have a unique opportunity to aid in the transition to a world with net - zero co2 emission.
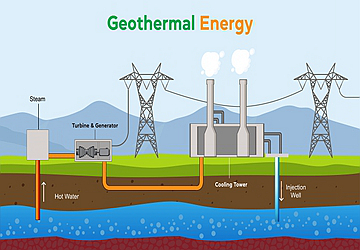
In their capacity as underwriters, insurers play a crucial role in easing the movement of funds toward mitigation initiatives by offering investors de-risking options. Geothermal energy investors, for instance, require risk transfer techniques to create an attractive risk-return profile. To overcome this obstacle, it is necessary to establish a pool that will offer de-risking options to facilitate private money to this vital renewable energy source.
On the other hand, insurers can use their underwriting to curb funding for the fossil fuel sector if they approach risk assessment and underwriting through an environmental, social, and governance (ESG) perspective rather than focus solely on the bottom lines.
As custodians of large amounts of long-term capital, insurers play a pivotal role in green investing's acceleration of the world's migration to a net-zero environment.
The recent formation of the United Nations Net-Zero Insurance Alliance indicates the growing global traction in this direction.
Adaptation
When dealing with the long-term effects of global warming, which is unfortunately inevitable, the insurance business may offer invaluable assistance because of its expertise in handling complicated long-term risks.
Knowing what risks exist and having reliable data and models to derive solutions is essential for effective risk management. The three basic pieces of data you should be aware of are the chance of a risk occurrence, the monetary losses it will inflict, and the secondary repercussions (such as an interruption in services) that will come from it. For a long time, insurance companies have relied on catastrophe models to simulate such effects and determine a fair price for the associated risk. Insurers can aid corporations and governments in making well-informed decisions about which resilience efforts to undertake by including climate risk modeling in these estimates.
The next step, after risk has been assessed, is risk management. One effective risk management strategy is to prearrange risk financing, while another is to invest in risk-reduction measures (such as irrigation schemes or flood defenses). The insurance sector provides a significant factor in both of these. Insurance company-backed risk transfer solutions are typically crucial for private financing to flow to appropriate infrastructure, just like mitigation initiatives. Moreover, the insurance market is built on the premise of providing a means to prearrange funding for potential risks. So, insurers must make the solutions that individuals, enterprises, and governments need.
What to do next
UNEP's Principles for Sustainable Insurance are one of the most significant worldwide efforts explicitly created for the insurance business (PSI). Environmental, social, and socioeconomic sustainability are all addressed, with a particular emphasis on the insurance that is both affordable and effective in mitigating risk and boosting the success of businesses.
Related Articles
- Do I Qualify For Life Insurance If I Have A Pre-Existing Disease
- What consumer benefits does life insurance offer?
- Reasons Why You Might Need To File A Travel Insurance Claim
- Why You Should Get Over 60s Life Insurance
- Everyone Should Have These Insurance Policies
- The essential functions of an insurance company
- What To Look For In Your Health Insurance Policy
- Getting Homeowners Insurance With a Bad Roof
- The Top 5 Life Insurance Mistakes That People Make
- What Is Insurance Proof?
Reading Rankings
- How to get lower health insurance premiums
- Mistakes you may make when applying for homeowners insurance
- Top Insurance Providers in the World
- What Is The Role Of A Home Insurance Broker?
- Lapses: An Overview
- What Is Umbrella Insurance? How Does It Work?
- How Covid-19 has affected the Insurance Industry
- Insurance role in addressing climate change and sustainable development
recommended
![]()
Why your auto insurance claim may not be accepted
![]()
What Is The Role Of A Home Insurance Broker?
![]()
Factors affecting travel insurance costs
![]()
Top 5 life insurance mistakes people make
![]()
Lapses: An Overview
![]()
Mistakes you may make when applying for homeowners insurance
![]()
Mistakes You Can Make When Claiming Your Homeowner's Insurance
You might like
- The Essential Insurance Covers Everyone Should Have
- Why Your Car Insurance Claim Might Not Be Accepted
- How Covid-19 has affected the Insurance Industry
- Top 5 Homeowners Insurance Mistakes You Should Avoid Making
- Reasons you may need to file a travel insurance claim
- Why Do You Need Travel Insurance?
- Everything you need to Know about Health Insurance Cover
- The essential functions of an insurance company







